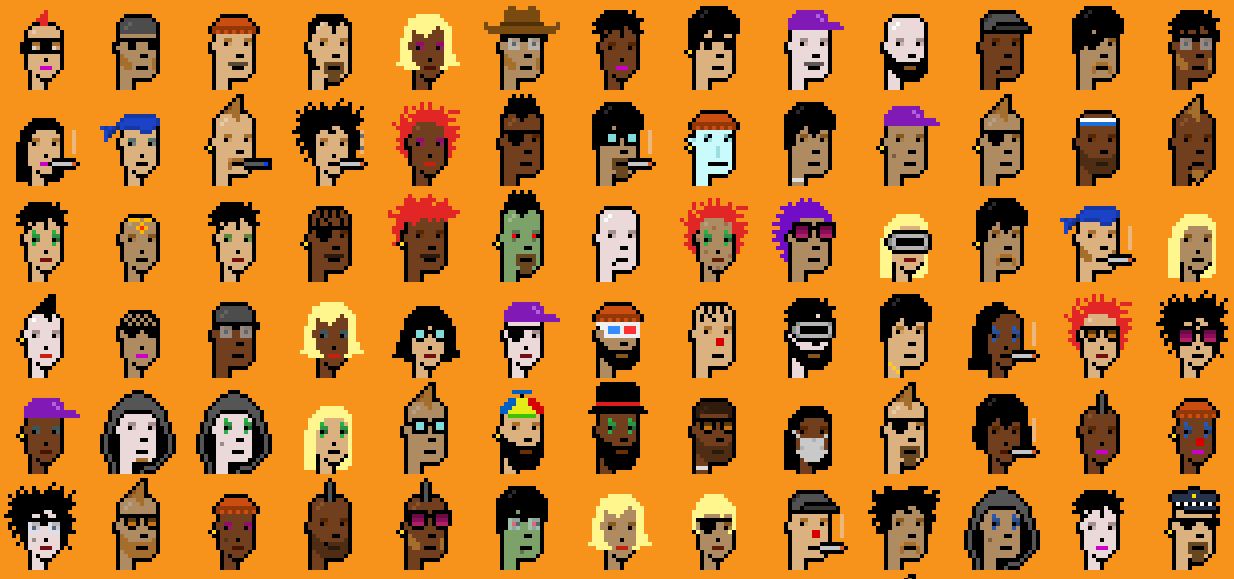
Bitcoin is often perceived as a store of value, an alternative to gold. However, with the emergence of the Ordinals protocol, Bitcoin is also becoming fertile ground for on-chain innovation and NFTs. In this article, we’ll explain Bitcoin’s Ordinals protocol, how it works and why it represents a significant breakthrough for Bitcoin.
What is Bitcoin’s Ordinals protocol?
On January 20, 2023, Bitcoin Core developer Casey Rodarmor announced on X that ” registrations were now available on the Bitcoin mainnet”. The protocol he had been developing for several months had finally seen the light of day under the name ofOrdinals.
The Ordinals theory
Each Bitcoin is divisible into 100 million units called satoshis (or sats). These units have been traded daily since 2009, making them difficult to identify and trace.
The Ordinals protocol allows each satoshi – Bitcoin’s smallest unit – to be numbered in their mining order and tracked individually. The name “Ordinal” refers to this ” first in, first out” scheme , based on the natural order of events.
This numbering introduces the concept of inscription, by which data (such as images, text or video) can be associated with each satoshi, transforming them into digital artifacts.
Registration
The most popular part of the Ordinals protocol is undoubtedly registrations. They enabledata to be permanently registered on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Data is limited by block size. They can be images, text files, audio clips, GIFs or even video games.
Registrations quickly flooded the Bitcoin blockchain, sometimes saturating the network and angering purists. But Ordinals paved the way for fungible tokens (BRC-20, Runes, rare sats) and non-fungible tokens (NFT) to be stored and traded on Bitcoin.
In short, Ordinals turns every satoshi into a digital collector’s item.
How does Ordinals work?
Let’s talk technology.
Historical background on Bitcoin
Ordinals is based on two major Bitcoin updates: SegWit and Taproot.
- SegWit (Segregated Witness) introduced in July 2017, reorganized transactions by moving part of the data into a separate database. This increased block size and improved transaction speed.
- Taproot, introduced in 2021, has added the ability to support lighter, more complex smart-contracts, stored in the witness data part of transactions.
Registration process
Casey Rodarmor used these updates to create Ordinals. The protocol makes it possible to store large amounts of data in a block and perform complex calculations.
The registration process takes place in several stages:
- Data preparation : Data to be entered is converted to hexadecimal format.
- Taproot script creation: Hexadecimal data are encapsulated in a Taproot script.
- Transaction creation :
- Commit transaction: Contains a hash reference to the Taproot script.
- Reveal transaction: Expends the output of the commit transaction by revealing the complete script, writing the data to the satoshi.
- Broadcasting and mining: Transactions are broadcast and confirmed by miners, integrating the data into the Bitcoin blockchain.
The opportunities offered by Ordinals
Digital asset creation
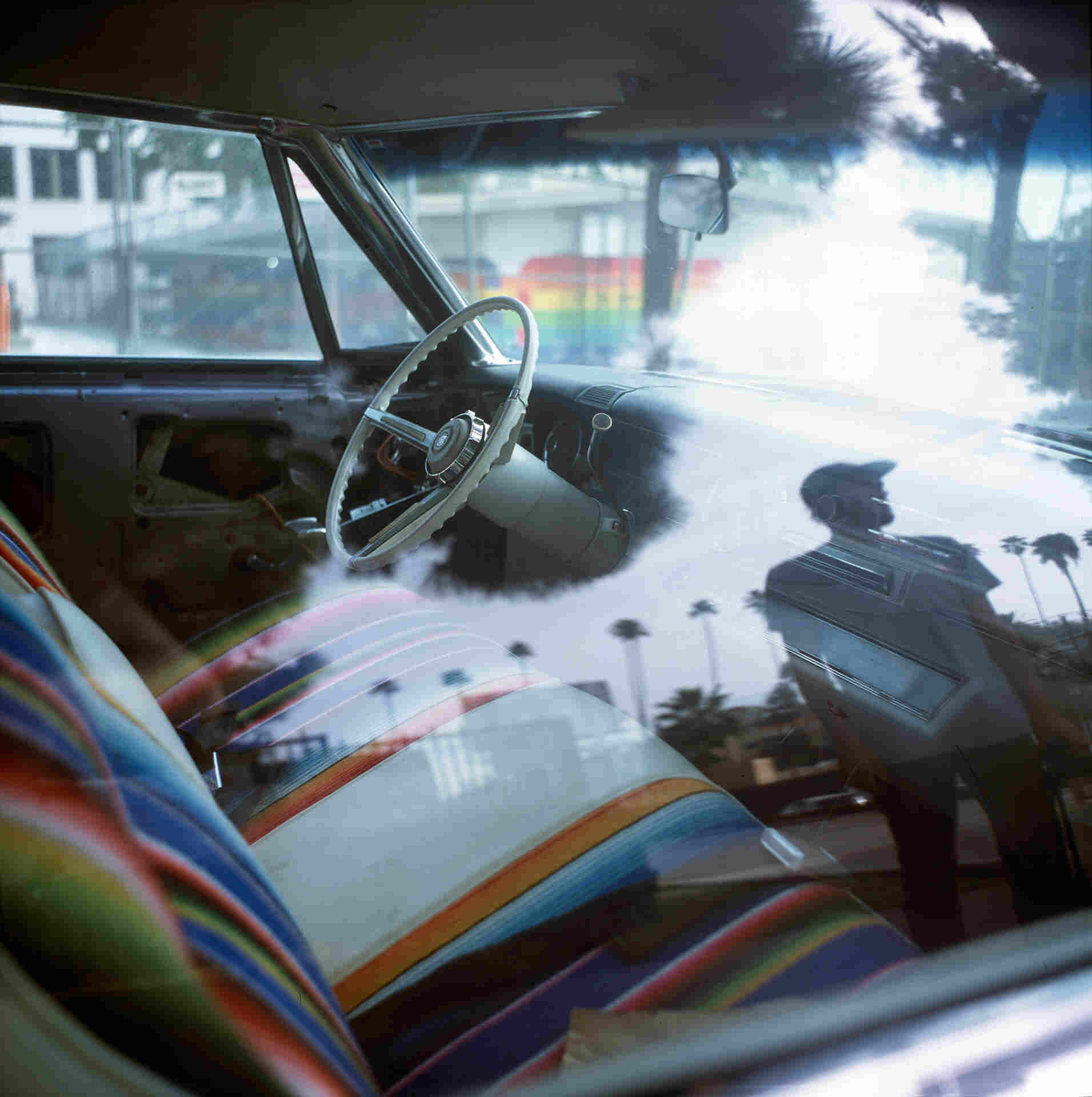
Artists can create and sell digital artworks inscribed on the Bitcoin blockchain, guaranteeing their authenticity and uniqueness. Collectors can buy and trade these artifacts, taking advantage of the network’s security. Many artists and projects have created their NFT collections on Bitcoin, and we present some of them to you from time to time on Symbole Art. Justin Aversano, for example, has created a collection of 136 prints of his photograph ” Colin in the car “.

Low registrations: the first registrations
Listings are numbered in ascending order. Today, there are over 70 million listings, and the number continues to grow. There is a market for the first numbered listings below 1000, 10,000 or 100,000. These are known as low registrations. Ordinals Tulips are a collection entirely within the first 10,000 listings.

Fungible tokens
With standards such as BRC-20 or Rune, it is possible to create fungible tokens on Bitcoin, facilitating the issuance of digital assets and integration into decentralized applications.
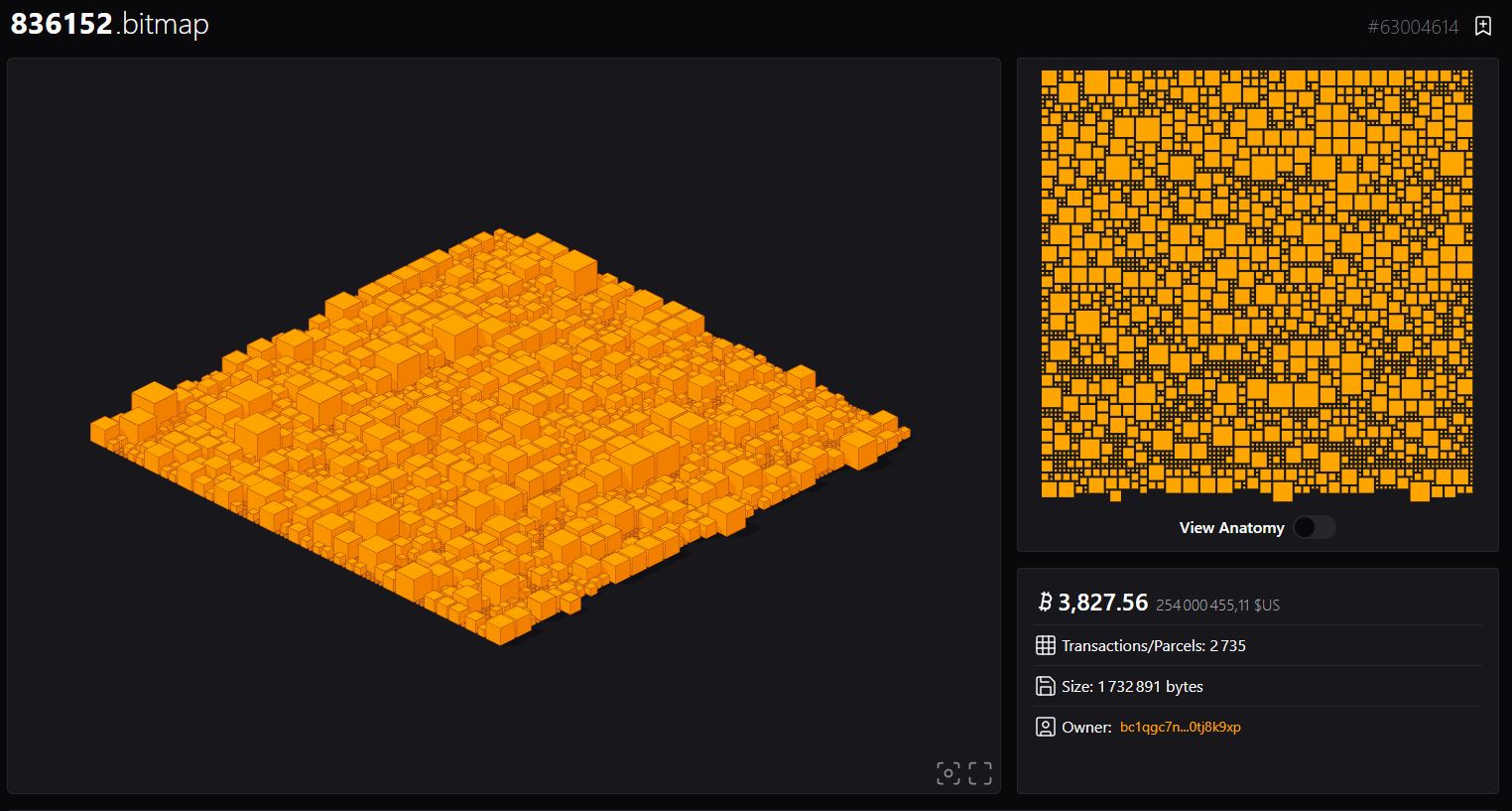
Bitmap: Bitcoin’s metaverse
Launched in 2023, Bitmap is a virtual environment built on all the blocks of the Bitcoin network. Each block is a district of the Bitcoin metaverse, with the transactions in each block corresponding to the parcels in each district. In this way, the configuration of the Bitcoin metaverse is governed by actual use of the network.
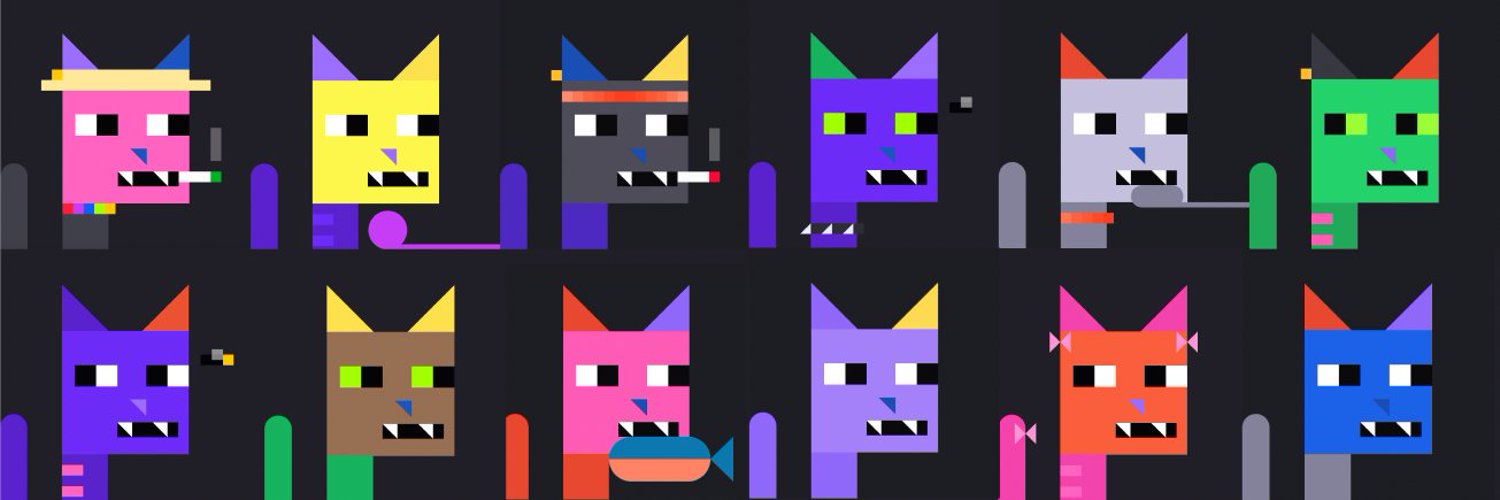
Natcats
The Natcats project uses a completely new approach to generate cat images(Natcats) from the specific data of certain Bitcoin transaction blocks. Block numbers determine the characteristics of each Natcat, introducing the concept of “dynamic rarity” and“unpublished features“.

Raresats
Different types of satoshis can be identified.
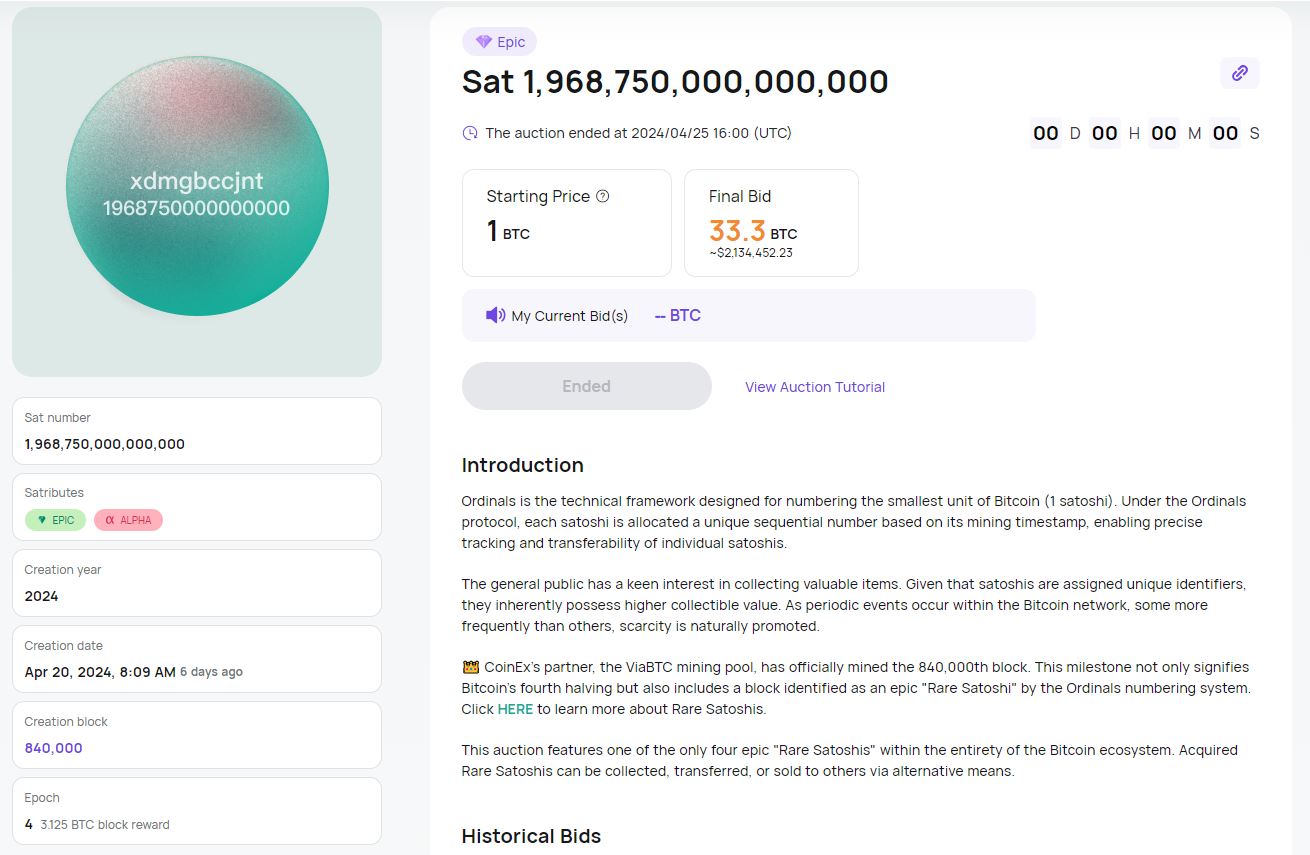
- Satoshis, which respond to periodic events in Bitcoin, such as the creation of new blocks, difficulty adjustments, halvings… The first satoshi following the last halving was sold for 33BTC or over 2 million dollars. Several marketplaces have emerged(Magisat, Magiceden, Sating) and Sotheby’s regularly organizes sales.
- Exotic satoshis linked to particular events in Bitcoin’s history (such as the satoshis of the first bitcoin transaction) or which have particular numerical properties, such as satoshis whose identifier is a palindrome.
Advantages and disadvantages of Bitcoin’s Ordinals protocol
Benefits
- Storage on the blockchain: Ensures immutability and independence from external storage solutions.
- Security: Benefit from the security of the Bitcoin network.
- Compatibility: Easily integrated with existing Bitcoin infrastructure.
- Innovation: Stimulates new applications and use cases within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Disadvantages
- Scalability problems: The Bitcoin blockchain is not optimized for high-frequency transactions.
- Size limitations: Restriction on the amount and complexity of data that can be entered.
- Simple functionality: advanced smart contracts difficult to set up.
- Environmental impact: Bitcoin mining requires a lot of energy.
- High costs: Transaction fees can be prohibitive for users.
The Ordinals debate
The arrival of the Ordinals protocol has created a heated debate among users, and rightly so!
Arguments Against
Some members of the Bitcoin community see Ordinals registrations as an attack on the network – yes, they do! They see the Ordinals protocol as exploiting a loophole to spam the Bitcoin blockchain. They fear that this will weigh down the network and increase transaction costs, making it more difficult to run complete nodes.
Arguments For
Others believe that Bitcoin is an open network where everyone should be able to use the blockchain as they see fit. The increase in transaction fees caused by Ordinals registrations is viewed positively by miners, as it increases their income and encourages them to further secure the network.
Conclusion
Ordinals represents a fascinating advance in the use of Bitcoin. This ingenious protocol enables digital artifacts to be created directly on the network. Although the protocol presents certain challenges, its potential for innovation and new applications for Bitcoin is undeniable.
Should Bitcoin remain focused on its monetary function, i.e. receiving-sending-storing Bitcoins? Or should its security and decentralization be put to use in other potential applications, such as those enabled by the Ordinals protocol? That’s the question. But whether you’re a maximalist bitcoiner, a digital artist or an investor, Ordinals deserves your attention. It redefines the ownership and exchange of digital assets, while exploiting the robustness and security of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Contact us to create a collection on Ordinals, acquire certain digital works or set up your own digital artifact management tools with Ordinals.

